- Barley Reference Transcript (BaRTv1.0) Dataset
Library construction and Illumina sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from c. 200 mg dissected frozen tissue from each sample using 2 ml TriReagent (Sigma) as recommended, with two additional phenol-chloroform purification steps followed by ethanol precipitation. RNAs were quality checked using the RNA 6000 Nano kit on a 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent). All RNA samples were judged high quality with an RNA Integrity Number (RIN) >8.
All RNA-seq libraries were constructed and run at The Genome Analysis Centre (Norwich, UK). The Illumina TruSeq RNA Sample preparation kit (Illumina Inc.) was used according to the manufacturer's protocol. In brief, poly-A containing mRNA molecules were purified from 1 µg total RNA using poly-T oligo attached magnetic beads using two rounds of purification. The purified mRNA was fragmented by addition of 5x fragmentation buffer (Illumina, Hayward, CA) and was heated at 94°C in a thermocycler for 8 minutes. The fragmentation yields fragments of ~250 bp. First strand cDNA was synthesised using random hexamers to eliminate the general bias towards 3-prime end of the transcript. Second strand cDNA synthesis was done by adding GEX second strand buffer (Illumina, Hayward, CA), dNTPs, RNaseH and DNA polymerase I followed by incubation for 2.5 h at 16°C. Second strand cDNA was further subjected to end repair, A-tailing, and adapter ligation with barcoded adapters in accordance with the manufacturer supplied protocols.
Purified cDNA templates were enriched by 15 cycles of PCR for 10 s at 98°C, 30 s at 60°C, and 30 s at 72°C using PCR Primer Mix Cocktail and PCR Master Mix (Illumina, Hayward, CA). The samples were cleaned using AMPure XP Beads and eluted in 30 µl Resuspension Buffer as per manufacturer's instructions (QIAGEN, CA). Purified cDNA libraries were quantified using Bioanalyzer DNA 100 Chip (Agilent Technology 2100 Bioanalyzer). The libraries were normalised to 10 nM and pooled equimolarly in pools of 8 samples per pool. Each pool of libraries was diluted to 2nM with NaOH solution and 5 µL of diluted library transferred into 995 µL HT1 (high salt buffer supplied by Illumina) to give a final concentration of 10 pM. 120 µL of normalised library was then transferred into a 200 µL strip tube and placed on ice before loading onto the Illumina cBot cluster generation system.
Each pool of libraries was clustered onto two lanes of an Illumina flowcell. Flow cells were clustered using TruSeq Paired-End Cluster Kit v3, following the Illumina PE_Amplification_Linearization_Blocking_Hybridisation_v8 recipe. On completion of the clustering procedure, the flow cell was loaded onto the Illumina HiSeq2000 instrument according to the manufacturer's instructions. A paired end sequencing protocol was performed generating 2 x 100bp reads using TruSeq SBS kit v3 sequencing chemistry, Illumina software HCS 1.4 and RTA 1.12.
| Tissue code | Tissue description | Paired-end reads | Sequencing Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMB | Embryo (germinating) | 142,000,000 |  |
| ROO | Root (10cm seedlings) | 192,000,000 | |
| LEA | Shoot (10cm seedlings) | 135,000,000 | |
| INF1 | Inflorescence (0.5cm) | 154,000,000 | |
| INF2 | Inflorescence (1-1.5cm) | 176,000,000 | |
| NOD | Tillers (3rd internode) | 557,000,000 | |
| CAR5 | Grain (5 DPA) | 149,000,000 | |
| CAR15 | Grain (15 DPA) | 166,000,000 | |
| ETI | Etiolated (10 day seedlings) | 134,000,000 | |
| LEM | Lemma (6 weeks pa) | 162,000,000 | |
| LOD | Lodicule (6 weeks pa) | 142,000,000 | |
| PAL | Palea (6 weeks pa) | 138,000,000 | |
| EPI | Epidermis (4 weeks) | 133,000,000 | |
| RAC | Rachis (5 weeks pa) | 144,000,000 | |
| ROO2 | Root (4 week seedling) | 144,000,000 | |
| SEN | Senescing leaf (2 months) | 117,000,000 | |
| Sequencing strategy for the 3 replicates. Paired-end 100 nucleotide RNA-seq reads on the Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform. Three biological replicates run in replicate-block design, 8-plex per lane per replicate set on duplicate lanes. | |||
Growing conditions
Plant material for EMB, ROO, LEA, INF1, INF2, and NOD samples was prepared from August to October in 2011 in the JHI glasshouse AO59, where no artificial lights were used and automatic watering was set up to keep compost moist. For the CAR5 and CAR15 samples, plants were grown under glasshouse conditions at IPK, Gatersleben, Germany. For growing plants, the left roller-bench was subdivided in the three areas A, B, C representing three replicates.
In the centre of each area, 10 cm from the bench surface, RFID temperature loggers miniNOMAD® (model OM-84-TMP from Omega Engineering Ltd (www.omega.co.uk )) were placed. Loggers were set to record temperatures every hour from 10:00 am August 3 to 10:00 am October 16. In total 1800 temperature measurements for each logger were recorded.
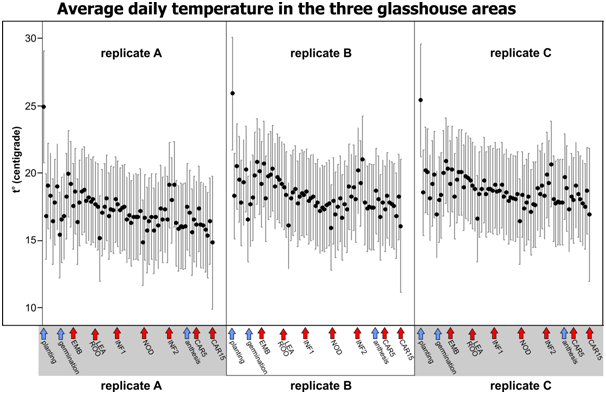 |
| Black dots show daily mean temperatures for 75 days of the experiment. Error bars are 95% Bonferroni corrected Confidence Intervals for the Mean (n=24). Arrows below show experiment start, anthesis (blue) and sampling points (red). |
|---|
Tissue sampling
About 400 cv Morex seeds were sterilized in a 1% bleach solution for 20 minutes, followed by extensive rinsing with tap water. After sterilization seeds were subdivided in three parts - one was used for germination on the plates to obtain EMB samples, the next was used to plant in the pots with perlite (for LEA and ROO samples), and the remaining in the pots with compost to grow plants for INF, NOD and CAR tissues. Tissue sampling always was between 10 and 11 am. All sampled tissues were flash frozen in liquid nitrogen and put in -80 C freezer for RNA extraction.
EMB
About 20 sterilized seeds were spread across 3 stacked sheets of wet filter paper and covered with 3 sheets of wet filter paper in the large 23x23 cm square petri dishes. Petri dishes were wrapped in the foil and placed in the same glasshouse area where seeds were planted. After four days of germination, embryonic tissue (coleoptile, mesocotyl and seminal roots) from nine similarly looking germinating seeds were dissected.
 |
| Tissue for the EMB prep |
|---|
LEA, ROO
Sampling of the LEA and ROO tissue was, when upper parts of the plants grown in pots with perlite reached about 10 cm length (17 days after planting). Plants were carefully removed from the pots, remains of the perlite were washed away, roots and shoots were separated by cutting just below and above the root/shoot junction. Remains of the embryo were not sampled. Roots and shoots from four plants were used per sampling.
 |
| Tissue for the LEA and ROO prep |
|---|
INF1, INF2
The main tillers of plants approximately one month old were used to dissect developing inflorescences (INF1). Only those inflorescences that were about 5 mm long were collected for RNA extraction. In total 15-20 inflorescences were dissected per sample. For obtaining 10-15 cm long inflorescences, main tillers from 50 day old plants were used.
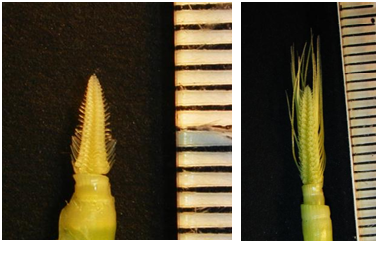 |
| Tissue for the INF1 (left) and INF2 (right) prep |
|---|
NOD
The third internode (4-6 cm long) was dissected from the 42 days old plants. Leaf blades and sheaths were removed, and the internode was cut out from just below the 4th and just above the 3rd nodes.
 |
| Tissue for the NOD prep |
|---|
CAR5, CAR15
To obtain developing caryopses (CAR), anthesis time was determined using about 2 months old plants by removing anthers from the central florets at the centre of the spike and examining their colour and determining whether they shed or not. Spikes with yellow anthers, but not shedding were marked and examined following few days for shedding to set the anthesis time. Five days after anthesis, three to five mm long caryopses (CAR5) were dissected from the central florets removed from the central part of the spike. Fifteen caryopses were collected per sample. Ten days later, ~10 mm caryopses were dissected from other set of spikes to obtain CAR15 samples.
 |
| Tissue for the CAR5 (left) and CAR15 (right) prep |
|---|
